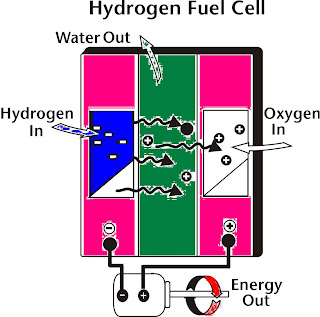
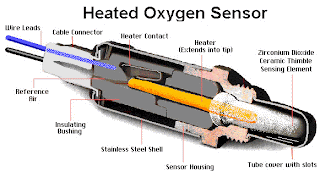
Wednesday, September 30, 2009
Monday, September 28, 2009
Sunday, September 27, 2009
Reducer Working Principles
ompressed Natural Gas flows from the tank to reducer through a special inlet nipple
(1). A filter (2) avoid solid particles to get into the reducer. 1st Reduction stage. The
High Pressure Valve (3), is controlled by High Pressure Membrane (4), this regulates
gas flow in the double Chamber of heating and expansion (5), where pressure is reduced
till 180 kPa. From here gas flows to the 2nd reduction stage. 2nd Reduction stage. It is
constituted by a Chamber (6), in comunication with the mixer, placed upstream the
throttle valve. The Membrane Unit (7), through the Valve (8) actuated by the Membrane
(9), feel the suction generated by engine pistons. The Valve (10), controlled by the just
mentioned unit, regulates gas flow from 1st stage Chambers (5) to 2nd stage Chamber (6),
where pressure is furtherly reduced till atmospheric (0±20 Pa). From here, gas flows into
intake manifold where it mixes with air coming from engine air filter, before flowing
inside cylinders ignition chamber.
“Stabilizer” device. The Stabilizing Valve (12) is controlled by the Membrane (11).
This valve permit to optimise the gas flow to the engine independently from engine rpm
values and from gas tank pressure. Shut off valve. A solenoid valve (19), controlled by
gas/petrol switcher, cuts gas flow from 1st to 2nd stage, at the same time the engine is
switched off. This happens both in case of intentional and casual switching off (in case
of damaging, accident, fuel completely consumed, etc. Heating system: CNG expansion
due to pressure reduction, has the effect of a temperature reduction. To avoid icing
inside the reducer, and to get the best efficiency from the fuel, the chambers where gas is
expanding, are heated up by engine cooling liquid (13). Carburetion adjustment
screws. Beside reducer there are 2 adjusting screws. The hexagonal M10 screw is the
Offset adjusting screw (14) and allow to modify the delivered gas quantity. The
hexagonal M8 screw is the Idle adjusting screw (15) and it’s usually closed. It must be
unscrewed only in the case the engine is switching off, in case of strong braking or fast
bend.
(1). A filter (2) avoid solid particles to get into the reducer. 1st Reduction stage. The
High Pressure Valve (3), is controlled by High Pressure Membrane (4), this regulates
gas flow in the double Chamber of heating and expansion (5), where pressure is reduced
till 180 kPa. From here gas flows to the 2nd reduction stage. 2nd Reduction stage. It is
constituted by a Chamber (6), in comunication with the mixer, placed upstream the
throttle valve. The Membrane Unit (7), through the Valve (8) actuated by the Membrane
(9), feel the suction generated by engine pistons. The Valve (10), controlled by the just
mentioned unit, regulates gas flow from 1st stage Chambers (5) to 2nd stage Chamber (6),
where pressure is furtherly reduced till atmospheric (0±20 Pa). From here, gas flows into
intake manifold where it mixes with air coming from engine air filter, before flowing
inside cylinders ignition chamber.
“Stabilizer” device. The Stabilizing Valve (12) is controlled by the Membrane (11).
This valve permit to optimise the gas flow to the engine independently from engine rpm
values and from gas tank pressure. Shut off valve. A solenoid valve (19), controlled by
gas/petrol switcher, cuts gas flow from 1st to 2nd stage, at the same time the engine is
switched off. This happens both in case of intentional and casual switching off (in case
of damaging, accident, fuel completely consumed, etc. Heating system: CNG expansion
due to pressure reduction, has the effect of a temperature reduction. To avoid icing
inside the reducer, and to get the best efficiency from the fuel, the chambers where gas is
expanding, are heated up by engine cooling liquid (13). Carburetion adjustment
screws. Beside reducer there are 2 adjusting screws. The hexagonal M10 screw is the
Offset adjusting screw (14) and allow to modify the delivered gas quantity. The
hexagonal M8 screw is the Idle adjusting screw (15) and it’s usually closed. It must be
unscrewed only in the case the engine is switching off, in case of strong braking or fast
bend.
Calculation new compression ratio for CNG engine
The main function of the piston modifications is to reduce the compression ratio of the engine.
Calculate the compression ratio for the gas converted engine, considering that the ideal compression
ratio must be:
- for N.A. CNG engines: 12 ÷ 13
- for turbocharged CNG engines: ~ 11,5
- for N.A. GPL engines: 9,5 ÷ 10
- for turbocharged GPL engines: 8,5 ÷ 9
The necessary data for the execution of the calculations of the new compression ratio are:
- original compression ratio of the engine
- displacement
- number of cylinders
- type of intake of air (turbo engine or N.A. engine)
- original dimensions of the original piston (with an original drawing)
- verify that the disposition of possible oil conduits in the original piston allows the necessary
workings (if it is possible, dissect an original piston).
COMPRESSION RATIO CALCULATION
(01). Calculate the UNITARY DISPLACEMENT (U):
U= TOTAL DISPLACEMENT / NUMBER OF CYLINDERS
(02). Calculate the VOLUME OF THE COMBUSTION CHAMBER when the piston is at the TDC (V2):
V2= UNITARY DISPLACEMENT / (ORIGINAL COMPRESSION RATIO – 1)
(03). Measure the volume of the original diesel bowl (Vbowl) filling it up with the water. Measure
the quantity of water that enters in the original diesel bowl.
 Subtract the volume of the ORIGINAL BOWL (Vbowl) to the VOLUME OF THE COMBUSTION CHAMBER (V2),
Subtract the volume of the ORIGINAL BOWL (Vbowl) to the VOLUME OF THE COMBUSTION CHAMBER (V2),
to find the volume included between the piston head and the engine head when the piston is at the TDC:
Vt = V2 – Vbowl

Take away 0,5 mm from the top of the piston and measure the new volume Vt:
Vt new = originalVt + (π * D2) / 4 * 0,5
 Calculate the volume of the bowl gas, working material until to the lateral (picture 04) and
Calculate the volume of the bowl gas, working material until to the lateral (picture 04) and
inferior (picture 05) tangent of the original diesel bowl.
Vgas bowl = (π * D2) / 4 * H



Calculate the new compression ratio with the formula:
ρ = U / (V2 gas) + 1
VERIFY IF THE NEW COMPRESSION RATIO IS ACCEPTABLE, LOOKING THE
VALUES WRITTEN AT THE BEGINNING OF THE PARAGRAPH. IF IT ISN’T
ACCEPTABLE, MODIFY THE VALUES OF D AND H (SEE THE PICTURE 06) IN
ORDER TO HAVE THE CORRECT VALUES TO OBTAIN A CORRECT
COMPRESSION RATIO
Calculate the compression ratio for the gas converted engine, considering that the ideal compression
ratio must be:
- for N.A. CNG engines: 12 ÷ 13
- for turbocharged CNG engines: ~ 11,5
- for N.A. GPL engines: 9,5 ÷ 10
- for turbocharged GPL engines: 8,5 ÷ 9
The necessary data for the execution of the calculations of the new compression ratio are:
- original compression ratio of the engine
- displacement
- number of cylinders
- type of intake of air (turbo engine or N.A. engine)
- original dimensions of the original piston (with an original drawing)
- verify that the disposition of possible oil conduits in the original piston allows the necessary
workings (if it is possible, dissect an original piston).
COMPRESSION RATIO CALCULATION
(01). Calculate the UNITARY DISPLACEMENT (U):
U= TOTAL DISPLACEMENT / NUMBER OF CYLINDERS
(02). Calculate the VOLUME OF THE COMBUSTION CHAMBER when the piston is at the TDC (V2):
V2= UNITARY DISPLACEMENT / (ORIGINAL COMPRESSION RATIO – 1)
(03). Measure the volume of the original diesel bowl (Vbowl) filling it up with the water. Measure
the quantity of water that enters in the original diesel bowl.
 Subtract the volume of the ORIGINAL BOWL (Vbowl) to the VOLUME OF THE COMBUSTION CHAMBER (V2),
Subtract the volume of the ORIGINAL BOWL (Vbowl) to the VOLUME OF THE COMBUSTION CHAMBER (V2),to find the volume included between the piston head and the engine head when the piston is at the TDC:
Vt = V2 – Vbowl

Take away 0,5 mm from the top of the piston and measure the new volume Vt:
Vt new = originalVt + (π * D2) / 4 * 0,5
 Calculate the volume of the bowl gas, working material until to the lateral (picture 04) and
Calculate the volume of the bowl gas, working material until to the lateral (picture 04) andinferior (picture 05) tangent of the original diesel bowl.
Vgas bowl = (π * D2) / 4 * H



Calculate the new compression ratio with the formula:
ρ = U / (V2 gas) + 1
VERIFY IF THE NEW COMPRESSION RATIO IS ACCEPTABLE, LOOKING THE
VALUES WRITTEN AT THE BEGINNING OF THE PARAGRAPH. IF IT ISN’T
ACCEPTABLE, MODIFY THE VALUES OF D AND H (SEE THE PICTURE 06) IN
ORDER TO HAVE THE CORRECT VALUES TO OBTAIN A CORRECT
COMPRESSION RATIO
Saturday, September 26, 2009
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)


 Toilets
Toilets Food court
Food court POS
POS BillBoard
BillBoard